





このアートワークの写真をもっと見たい場合はお知らせください。
- 仕事の裏側 / 仕事の側面
- 細部 / 署名 / アートワークの表面またはテクスチャ
- アートワーク イン シチュエーション, その他...
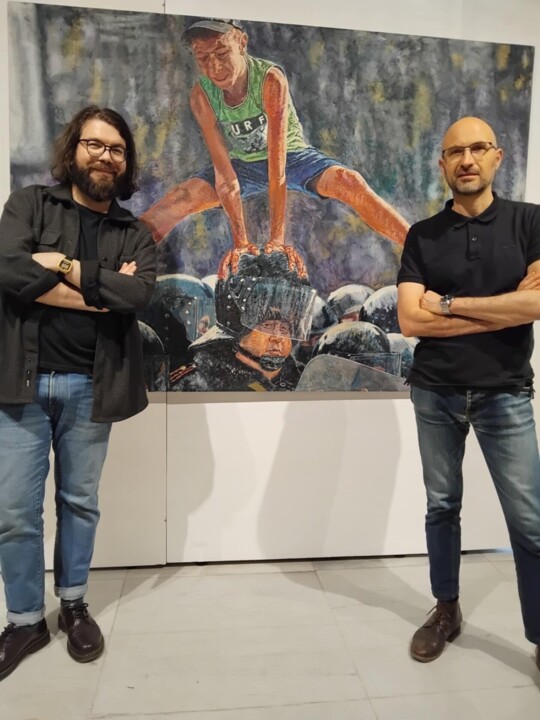
I Don't Jump On Command, I Command The Jump (2025) 絵画 Anton Terziev によって
詳細情報
- 包装 (ボックスまたはカートンのパッケージ) すべてのアートワークは、慎重に保護され、保険がかけられたプレミアムキャリアで出荷されます。
- モニタリング 購入者への引き渡しまでのご注文の追跡. 追跡番号が提供されるので、リアルタイムで荷物を追跡できます。
- 遅らせる 3〜7日で世界中に配達 (見積もり)
- 税関は含まれていません 価格には通関手数料は含まれていません。ほとんどの国ではオリジナルのアートワークに輸入税はありませんが、減額されたVATを支払う必要がある場合があります。通関手数料(ある場合)は、到着時に税関が計算し、運送業者が別途請求します。
詳細情報
- 追跡可能なオンラインCertificateof Authenticity 真正性証明書は、アートワークコードをスキャンすることにより、いつでもオンラインで確認できます。
- 認証評価のアーティスト 専門家は芸術家の仕事やキャリアを研究し、その後独立し、信頼性の平均価格の値を設定する。平均価格の値は、一定期間の価格帯でのアーティストsituates。専門家はまた、特定の作業のためのより正確な見積もりを確立するために求められることがあります。
詳細情報
SSL証明書と100%安全な支払い + 3D Secure.
詳細情報
この画像を Web サイトやコミュニケーションに使用したり、派生製品を販売したりするには、ライセンスを購入してください。
Usage: Webライセンス
| 1500 px | ||

|
1030 px |
| ファイルの寸法 (px) | 1500x1030 |
| 世界中で使用 | はい |
| マルチサポートで使用 | はい |
| あらゆるタイプのメディアで使用 | はい |
| 再販の権利 | ノー |
| プリントの最大数 | 0 (Zero) |
| 販売を目的とした製品 | ノー |
購入後すぐにダウンロード
この画像はライセンス付きでダウンロードできます: いつでもダウンロードできます。
制限
ArtMajeurのすべての画像は、アーティストによって作成されたオリジナルの芸術作品であり、すべての権利は厳密に留保されています。ライセンスの取得により、ライセンスの条件に基づいて画像を使用または悪用する権利が与えられます。プロジェクトに完全にフィットするように画像のリフレーミングやリフォーカスなどの小さな変更を加えることは可能ですが、元の作品の完全性を損なう可能性のある変更(形状の変更、アーティストから事前に書面による許可を得ていない限り、歪み、カット、色の変更、要素の追加など)。
カスタムライセンス
使用法が当社の標準ライセンスでカバーされていない場合は、カスタムライセンスについてお問い合わせください。
アートイメージバンク-
オリジナルのアートワーク (One Of A Kind)
絵画,
キャンバスの
オイル
- 寸法 高さ 57.1in, 幅 76.8in
- フレーミング このアートワークは額装されていません
- カテゴリ 絵画 $20,000未満 造形美術 政治
The painting’s focal point is a youthful figure leaping over a heavily armored officer. The choice to place this figure mid-action—hands pressing atop the helmet—lends the painting a kinetic energy. Terziev halts a fleeting instant, reminiscent of photojournalistic “freeze-frames,” yet renders it in a painterly style. This tension between photo-like immediacy and the expressiveness of oil paint gives the scene both documentary clarity and a certain timelessness.
The tight framing around the main subjects emphasizes the confrontation. In the background, a phalanx of similarly clad officers recedes into an indistinct crowd, hinting at a broader social or political apparatus. The dynamic pose of the young figure—legs extended, arms bearing weight—cuts diagonally across the canvas, drawing the viewer’s eye from the figure’s face to the helmet below. This diagonal thrust is a compositional technique often employed to heighten drama, recalling, for instance, the angled bodies in Eugène Delacroix’s “Liberty Leading the People.” Terziev appears to favor a saturated palette: the vivid greens of the protester’s shirt and the deep blacks of the riot gear contrast sharply. The background’s muddled, smoky hues evoke tension and turmoil. Despite this gloom, the central figure seems illuminated—whether literally or symbolically—standing out against the massed uniforms. This painterly contrast underscores a classic artistic trope: the individual’s bright presence opposing a darker, more uniform collective force.
At first glance, the painting comments on the power dynamic between state authority (the officer in riot gear) and the individual (the agile figure vaulting over him). The act of physically leaping above the officer’s head becomes a metaphor for transcending imposed limits or commands. It suggests a reversal of typical power structures: the officer, usually the figure of control, is relegated to a support—albeit involuntarily.
The subject’s youthful appearance adds another layer of resonance. Depicting a young individual in direct, physical interaction with law enforcement draws upon an established tradition of protest imagery, where youth movements have historically galvanized political change. This generational tension recalls iconic photographs from the 20th and 21st centuries, in which young protesters often become the faces of revolution or societal critique.
The painting also alludes to the idea of the human body as a site of protest. The choice to vault, rather than to push or to attack, speaks to a form of resistance that is acrobatic, creative, and emblematic of personal freedom. It contrasts with the rigid, disciplined body language of the officers. In this sense, the work resonates with a lineage of politically charged performance art and photography, wherein gestures of dance or athleticism become statements of defiance.
While Terziev’s style is distinct from the Romantic or Baroque, the thematic of state power versus individual vulnerability recalls Francisco Goya’s **“The Third of May 1808.”** There, too, we see a focus on the human cost of political strife. Goya’s unflinching look at violence resonates in Terziev’s more contemporary depiction of confrontation, even if the latter is less about overt bloodshed and more about tension and symbolic subversion.
More directly, the painting aligns with 20th- and 21st-century traditions of politically engaged art—think of works by artists such as Banksy or Ai Weiwei, who fuse bold imagery with pointed social critique. Terziev’s piece, however, remains firmly in the realm of painting, bringing to mind large-scale compositions that historically served as calls to action or documentation of collective struggle.
Although the painting captures a realistic moment, the brushwork seems deliberately visible—especially in the musculature of the figure and the textured rendering of the riot gear. This blend of realism and expressionistic brush handling imparts an emotive quality. The painting avoids the polished sheen of hyperrealism, instead embracing a slightly raw surface that mirrors the rawness of civil strife.
As a large-scale work, the painting presumably envelops the viewer, magnifying the tension between protester and authority. Large canvases historically lend a monumental aura to their subject matter—an effect that can transform a single leap into a sweeping allegory of societal power struggles.
I Don’t Jump On Command, I Command the Jump” stands as a compelling example of contemporary political painting. Through a vividly captured, acrobatic gesture of defiance, Anton Terziev provokes reflection on youth, power, and the state’s response to public dissent. The painting’s dynamic composition, saturated color contrasts, and expressive brushwork imbue it with a timeless urgency. In art historical terms, it joins a lineage of works that memorialize moments of societal upheaval—echoing both the immediacy of photojournalism and the grandeur of historical painting.
By framing the tension between the individual and the forces of authority in a single, frozen leap, Terziev not only documents a poignant political instant but also suggests the broader, universal spirit of protest that transcends geographic and temporal boundaries. The painting thus resonates as a contemporary emblem of resilience—both a snapshot of a specific socio-political climate and a more enduring symbol of the human impulse to rise above constraints.
関連テーマ
ブルガリアの現代芸術家、アントン・テルジエフは、芸術的ツールとして鋭い皮肉を使い、現代のさまざまな主題に取り組む達人です。彼の作品は、厳格で批判的なイメージを伝える図像を多用しているのが特徴です。アントンは芸術レパートリーの中で、賭け金、スキル、ストーリーテリングの要素を巧みに織り交ぜ、その結果、社会的コメント、ユーモア、アーティストの状態についてのメッセージを繊細に伝える具象的な現代美術が生まれました。
アントン・テルジエフは、2 つの異なるソースからインスピレーションを得ています。第一に、彼のアートは多くの場合、現実の出来事から生まれ、彼の創造的なプロセスを刺激する形で彼の周りで展開されます。第二に、彼の想像力は彼の作品において極めて重要な役割を果たしており、鮮やかで示唆に富んだイメージを生み出すことができます。彼の作品には、映画や本から抽出したポップ カルチャーの微妙な要素があしらわれています。すべての作品には物語が埋め込まれており、鑑賞者を圧倒することなく豊かな体験をもたらすメタテキストです。アントンは、優れた芸術は柔らかく、しかし効果的に伝えるものであると信じています。
アントンの作品の特徴は、観客に無限の驚異の感覚を残そうとする彼の揺るぎない取り組みです。彼の作品は鑑賞者に芸術との対話を促し、彼が提示する物語を解釈し、疑問を持ち、探求することを促します。作品に最適なタイトルを選ぶのは、彼が文学、映画、音楽からインスピレーションを得て取り組む課題です。
アントン・テルジエフの画家としてのキャリアは、作家としての彼のアイデンティティと複雑に絡み合っています。彼のアイデアは絵画や美術品という形で形になり、彼の多彩な才能が反映されています。絵画を超えて、彼はパフォーマンス、映画製作、デザインを通じて芸術的ビジョンに命を吹き込み、創造的な表現に対する多面的なアプローチを示しています。
-
国籍:
ブルガリア

- 生年月日 : 1977
- 芸術的ドメイン: プロのアーティストによる作品,
- グループ: プロのアーティスト 現代ブルガリアの芸術家















